The size of a protein depends upon the type and number of amino acids. Each protein has specific properties that are determined by the number and specific sequence of amino acids in a molecule and its shape.
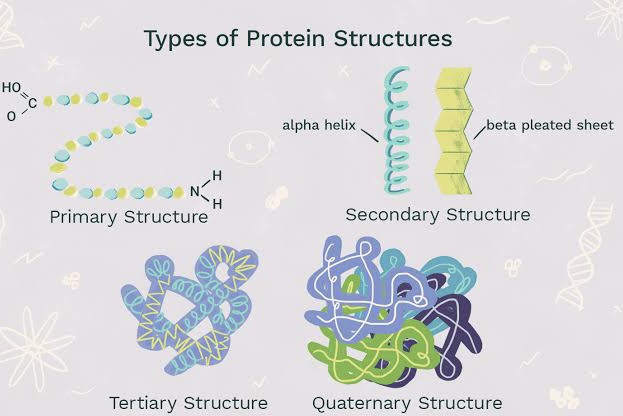
There are four levels of organizations of proteins.
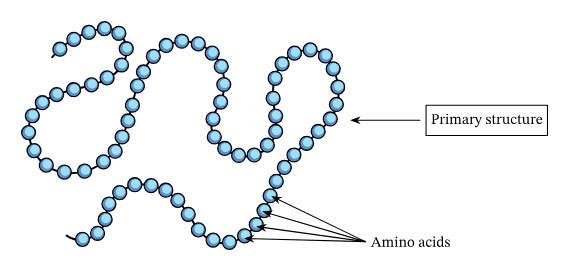
Primary structure :
A linear structure of protein that shows the number amd sequence of amino avids in a protein is known as primary structure.
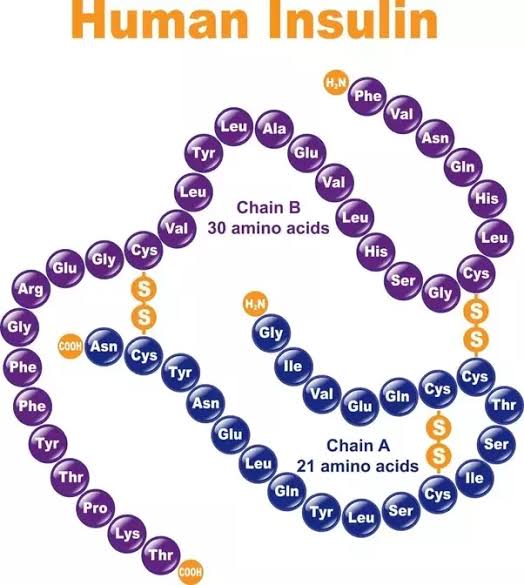
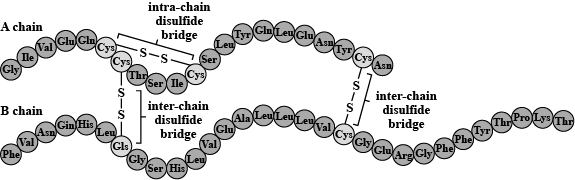
E.g. insulin is consist of 51 amino acids in 2 chains. One of the chain has 21 amino acid and other chain has 30 amino acids and both chaim are held togather by disulphide bridge.
Hemoglobin is composed of 4 chains, two alpha and two beta chains. Each alpha chain contains 141 amino acids, and each beta chain contains 146 amino acids.
The arrangement of amino acids is specific like in sickle cell hemoglobin the 6 amino acid glutamic acid is replaced by valine and thus due to this the hemoglobin fails to carry out any sufficient oxygen leading to death of patient.
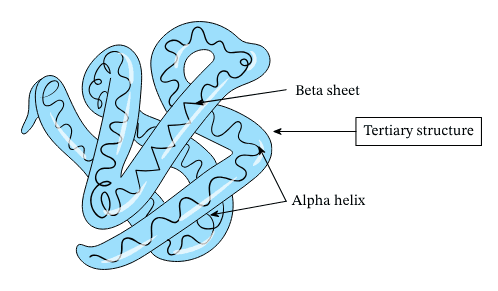
Secondary structure :
A coiled structure of protein is known ad secondary structure. One of the common secondary structure is alpha helix. It involves the spiral formatiom of the basic polypeptide chain.
The alpha helix is very uniform geometric structure with 3.6 amino acid in each turn of the helix. The helical structure is due to the formation of hydrogen bonds with amino acid molecules in different turns of the spiral.
Beta plated sheet: in this case the polypeptide chains are more extended and lie parallel with hydrogen bonding between chains.
Tertiary structure :
A coiled structure of protein that is further coiled or folded on itself is known as tertiary structure.
Quarternary structure :
An aggregation of the tertiary protein structure held togather is known as quarternary structure of protein.
Haemoglobin exibits this structure.







0 Comments