What is metabolism?
Biochemistry
Biochemistry is
the branch of biology that deals with the study of chemical components and
chemical processes in living organisms.
It encompasses a
wide range of fields including molecular biology, genetics, pharmacology, and
physiology. Biochemists study the chemical reactions and pathways that occur
within cells and organisms, and the molecules involved in these processes.
Biochemistry
plays a crucial role in understanding the fundamental processes of life, and
has important applications in medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
All living things
are made-up of certain chemical compounds which are generally classified as
organic and inorganic compounds.
Difference between chemical composition
of bacterial and mammalian cells
Water:
70% in
both bacterial and mammalian cells.
Protein:
15% in
bacterial cell an 18% in mammalian cell.
Carbohydrates:
3% in
bacterial cell and 4% in mammalian cell.
Lipids:
2% in bacterial
cell and 3% in mammalian cell.
DNA:
1% in
bacterial cell and 0.25% in mammalian cell.
RNA:
6% in
bacterial cell and 1.1% in mammalian cell.
Other organic
molecules:
(Enzymes,
hormones, metabolites) 2% in both bacterial and million cell.
Inorganic ions:
1% in
both bacterial and Mammalian cell.
What is
metabolism?
Metabolism
All the chemical
reactions take place within a cell or collectively called metabolism.
Metabolism refers
to the set of chemical reactions that occur within living organisms to sustain
life. These reactions involve the breakdown of molecules (catabolism) to
release energy and the synthesis of molecules (anabolism) to build and maintain
cellular structures and functions.
Metabolism is
regulated by a complex network of enzymes and hormones that control the rate
and direction of metabolic pathways. These pathways are highly interconnected
and can be influenced by factors such as diet, exercise, and stress.
Disruptions in
metabolism can lead to a wide range of diseases and disorders, such as obesity,
diabetes, and cancer. Understanding the mechanisms of metabolism is crucial for
developing effective treatments for these conditions.
Metabolism is a
fundamental process that allows living organisms to survive and thrive, and is
a key area of research in biochemistry and molecular biology.
classification of metabolism
Metabolic
processes are characterised as anabolism and catabolism
What is anabolic
reactions?
Anabolic reactions:
Reactions in
which simpler substances are combined to form complex substances are known as
anabolic reactions.
These reactions
require energy input, typically in the form of ATP, and involve the formation
of chemical bonds. Anabolic reactions are the opposite of catabolic reactions,
which break down complex molecules into simpler ones.
Anabolic
reactions need energy.
Examples of anabolic reactions
The process of
building proteins from amino acids. This process requires energy and is
essential for growth and repair of tissues.
The process by
which plants use sunlight to synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and
water.
The synthesis of
fats from simple precursors such as glucose.
The synthesis of
glycogen from glucose.
The process of
building DNA and RNA from nucleotides.
Anabolic
reactions are important for maintaining and building the complex molecules that
make up living organisms. They are essential for growth, repair, and
maintenance of tissues, and for the production of energy stores in the form of
glycogen and fat.
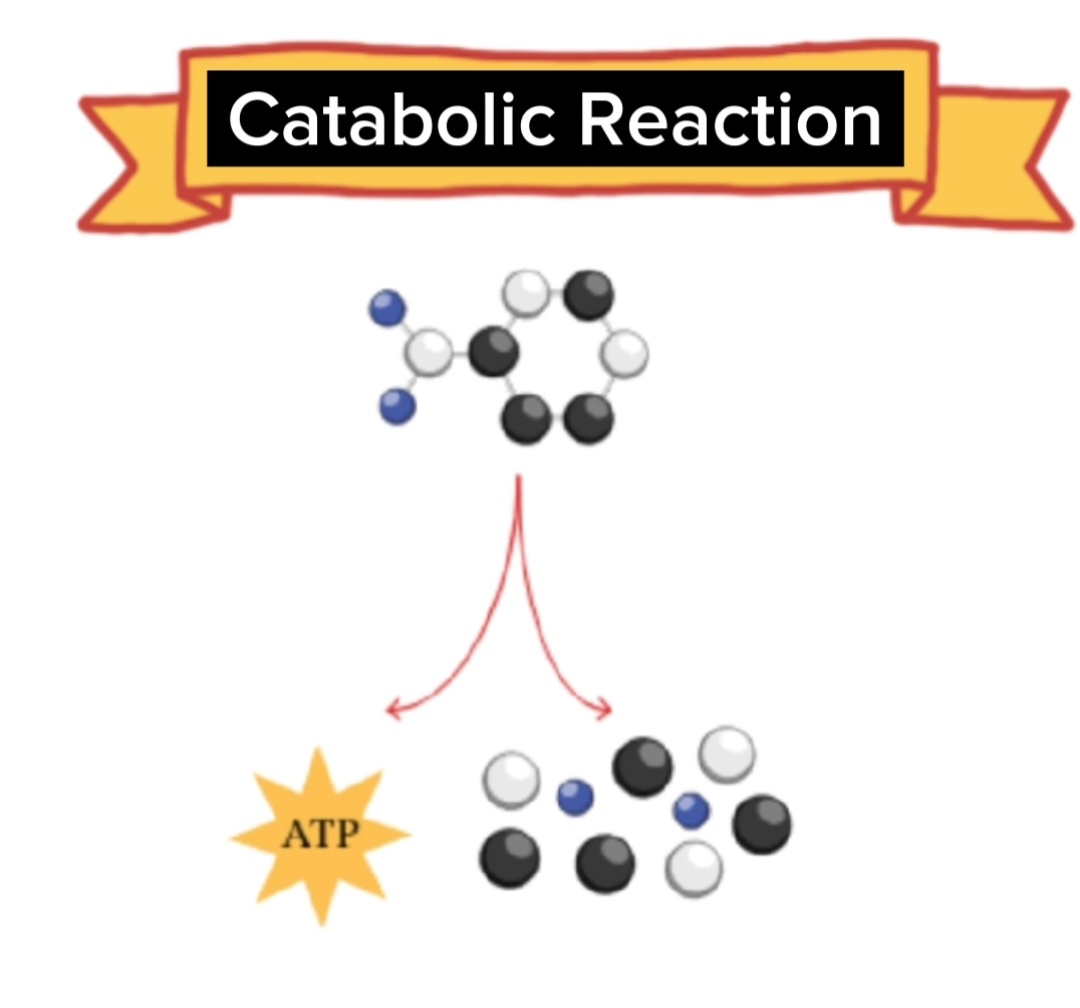
What is catabolic
reactions?
Catabolic reactions:
Catabolic
reactions are metabolic processes that break down complex molecules into
simpler ones, releasing energy in the process. These reactions are the opposite
of anabolic reactions, which build complex molecules from simpler ones.
Catabolic
reactions release energy.
Examples of catabolic reactions
The method by
which cells break glucose to make energy in the form of ATP.
The breakdown of
food molecules into smaller components such as glucose, amino acids, and fatty
acids.
The breakdown of
glucose into pyruvate, which can then enter cellular respiration.
The breaking of
fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
The breakdown of
proteins into amino acids.
Catabolic
reactions are important for generating energy and breaking down molecules that
are no longer needed by the body. The energy released during catabolism is used
to power anabolic reactions that build new molecules and perform other cellular
processes.
Importance of metabolism:
Metabolism is responsible
for converting the energy stored in nutrients such as glucose, fats, and
proteins into ATP, which is the primary energy currency of cells. Without
metabolism, cells would not be able to produce the energy needed to carry out
their functions.
Metabolism is
involved in the synthesis of complex molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids,
and lipids. These molecules are used to build and repair cells and tissues, and
to maintain the body’s structure and function.
Metabolism is
also responsible for breaking down and eliminating waste products from the
body. This includes the breakdown of toxins and other harmful substances, as
well as the removal of carbon dioxide and other metabolic waste products.
Metabolism is
involved in the regulation of many physiological processes, including the
regulation of body temperature, blood sugar levels, and hormone levels.
Metabolism allows
organisms to adapt to changing environmental conditions by regulating the
synthesis and breakdown of different molecules as needed.
Learn more
What is
biological molecules?
What is
biochemistry?
Comparison of the
chemical composition of bacterial and mammalian cells
Difference
between the chemical composition of bacterial and mammalian cells
what is the
difference between Bacterial and mammalian cells?
What is
metabolism?
Classification of
metabolism
Characterization
of metabolism
Types of
metabolism
Classes of
metabolism
What is anabolic
reactions?
Does anabolic
reactions need energy?
What is catabolic
reactions?
Does catabolic
reactions release energy?
Examples of
anabolic reactions
Examples of
catabolic reactions
Examples of
catabolic and anabolic reactions







0 Comments