Chemical Bond:
Chemical
bond is the force that holds two or more than two atoms , ions or molecules together
is called chemical bond.
In
chemical bond formation rearrangement of electrons occurs.
Cause of chemical bonding:
The
tendency of an element to attain a stable electronic configuration is the cause
of chemical bonding.
The
chemical reactivity of elements depends upon their characteristic electronic
configuration.
On
the basis of chemical reactivity,
elements are classified into two types
1 Inert elements:
The inert elements have
stable electronic configuration of valence shell. show little chemical
reactivity. However Xe forms certain compounds like XeF2, XeO3, etc. A noble
gas doesn't react with another noble gas. The cause of chemical inertness is
the filled outermost shell of each noble gas.
2 Reactive elements:
These elements combine with the other elements in order to
attain the nearest inert gas configuration .
E.g. Hydrogen shares one electron with another hydrogen and
resembles helium with two electrons. Na loses one electron and resembles neon
with ten electrons .Chlorine gains one electron and resembles Argon with
eighteen.* chemical bonding
Types of Bonds:
On
the basis of lewis concept, the different types of bonds are as follows
· ● Ionic bond
· ● Covalent bond
Types of covalent bond
· ● Non-polar covalent bonds
· ● Polar covalent bonds
· ● Single covalent bonds
· ● Double covalent bonds
· ● Triple covalent bonds
· ● Co-ordinate covalent bonds
Ionic Bond:
The
type of chemical bond that is formed by complete transfer of electrons is known
as ionic bond.
This
type of bond is formed between elements with low ionization energy and elements
with high electron affinity.
Ionic
compounds are also known as electrovalent compounds. In these compounds there
are a strong electrostatic force of attraction between cations and anions which
is responsible for stability of these compounds. Because ions exert forces in
all directions that’s why ionic bond is non-directional.* chemical bonding
Covalent bond:
A
covalent bond is defined as the type of chemical bond that is formed through
mutual sharing of electrons between the two atoms.
A
covalent bond may be non-polar or polar in character.
Types of covalent bond:
Non-polar covalent bond:
In
non-polar covalent bond electrons are equally shared between two atoms, and
bond is said to be non-polar covalent bond.
E.g.
H.........●■.........H
Polar covalent bond:
In
polar covalent bond electrons are not equally shared between two atoms, and bond is said to be polar covalent bond.
E.g.
H...........●■...Cl
H..............●■..F
The
shared pair of electrons is displaced towards the more electronegative
atom.this make one end of molecule partially positive and other end of molecule
partially negative that’s why it is called polar molecules.
Because
polar bond has ionic character that’s why it is also called partially ionic
bond.* chemical bonding
Single covalent bond:
It
is a type of covalent bond that is formed through sharing of one electron pair.
E.g.
C-C
Double covalent bond:
It
is the type of covalent bond that is formed through sharing of two electron
pairs.
E.g.
C=C
Triple covalent bond:
It
is the type of covalent bond that is formed through sharing of three electron pairs.
E.g.
C _=
C
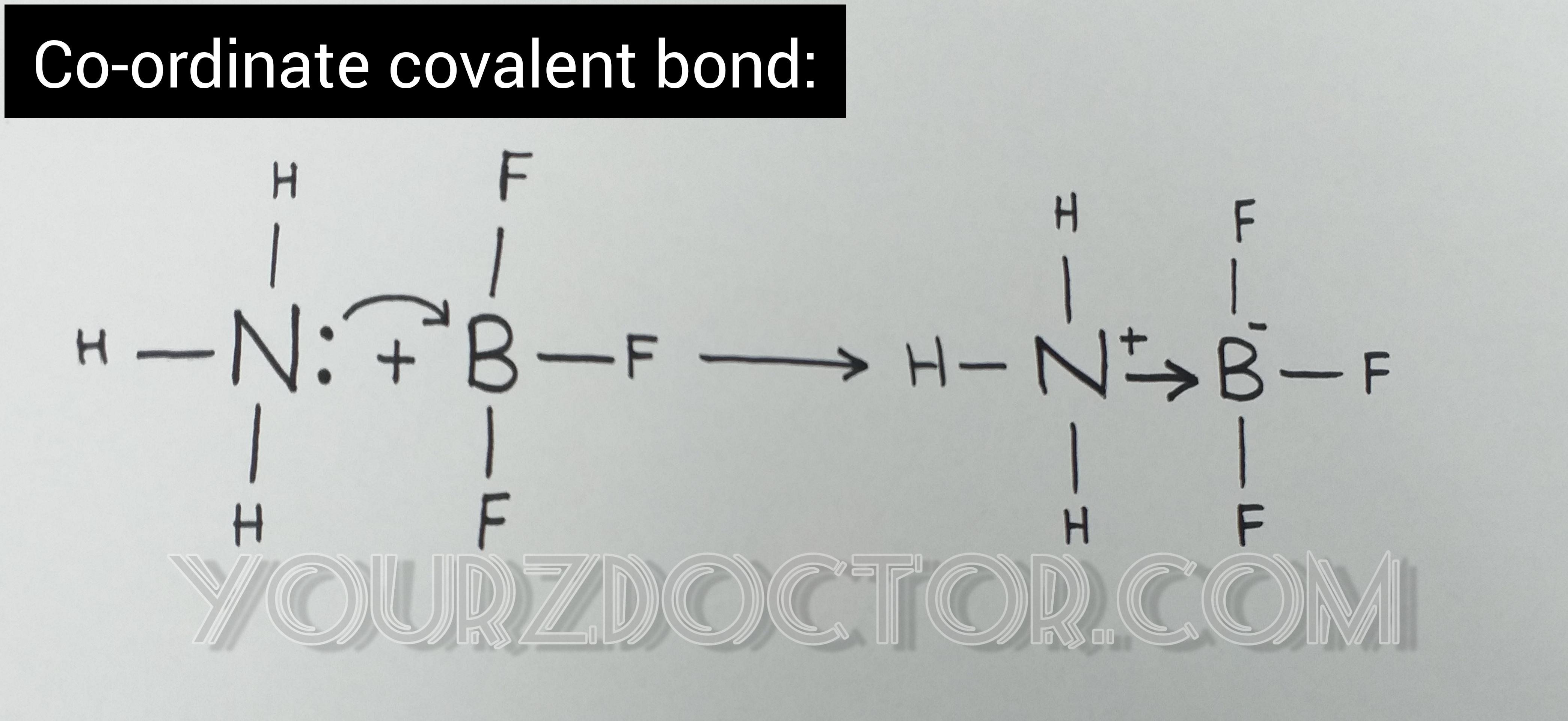
Co-ordinate covalent bond:
Co-ordinate
covalent bond is also called dative bond.
A
co-ordinate covalent bond is formed between two atoms when the shared pair of
electrons is donated by one of the bonded atoms.
An
example of co-ordinate covalent bond formation is that formed between NH3 and
BF3.
The
element that donates electrons is known as donor and the one that accepts is
known as acceptor.
Co-ordinate
covalent bond is represented by arrow head à
that runs from donor to acceptor. The complex produced is overall neutral and
charges are indicated on N and B atoms.* chemical bonding
Learn more
Search Tags
What is chemical bond?
Inert elements and reactive elements
What is ionic bond?
What is covalent bond?
What are the 4 types of chemical bonding?
What is chemical bonding and why is it important?





0 Comments