Concept of hybridization:
When
carbon forms methane , then the bond strength of the bond formed between 2s of C
and 1s of H must be different from that of the other bonds due to difference in
shapes and energies. But experimentally it was seen that bond strength of all the
4 bonds is the same, this show that orbitals must have mixed to form orbitals of
same shapes and energies.
Hybridization:
The process
of mixing of orbitals of different shapes and energies to form equivalent orbitals
of the same shapes and energies is known as hybridization.
Types of hybridization:
1) Sp3
hybridization
2) Sp2
hybridization
3) Sp
hybridization
sp3 hybridization:
The process
in which one s and three p orbitals mix to form a new set of four
equivalent sp3 hybrid orbitals is known as sp3 hybridization.
E.g.
Methane, ethane, ammonia and water are formed through this
type of hybridization.
In sp3
hybridization there is the promotion of electrons from s orbital to p orbital and
by hybridization making the 4 sp3 orbitals.* types of hybridization
Sp2 hybridization:
The process in which one s and two p orbitals mix to form a new set of three equivalent sp2 hybrid orbitals is known as sp2 hybridization.
E.g.
Ethene
and boron triflouride are formed through this type of hybridization.
The purpose
of leaving one P orbital unhybrid is to form pi bond. The number of unhybrid orbitals
is equal to the number of pi bonds.* types of hybridization
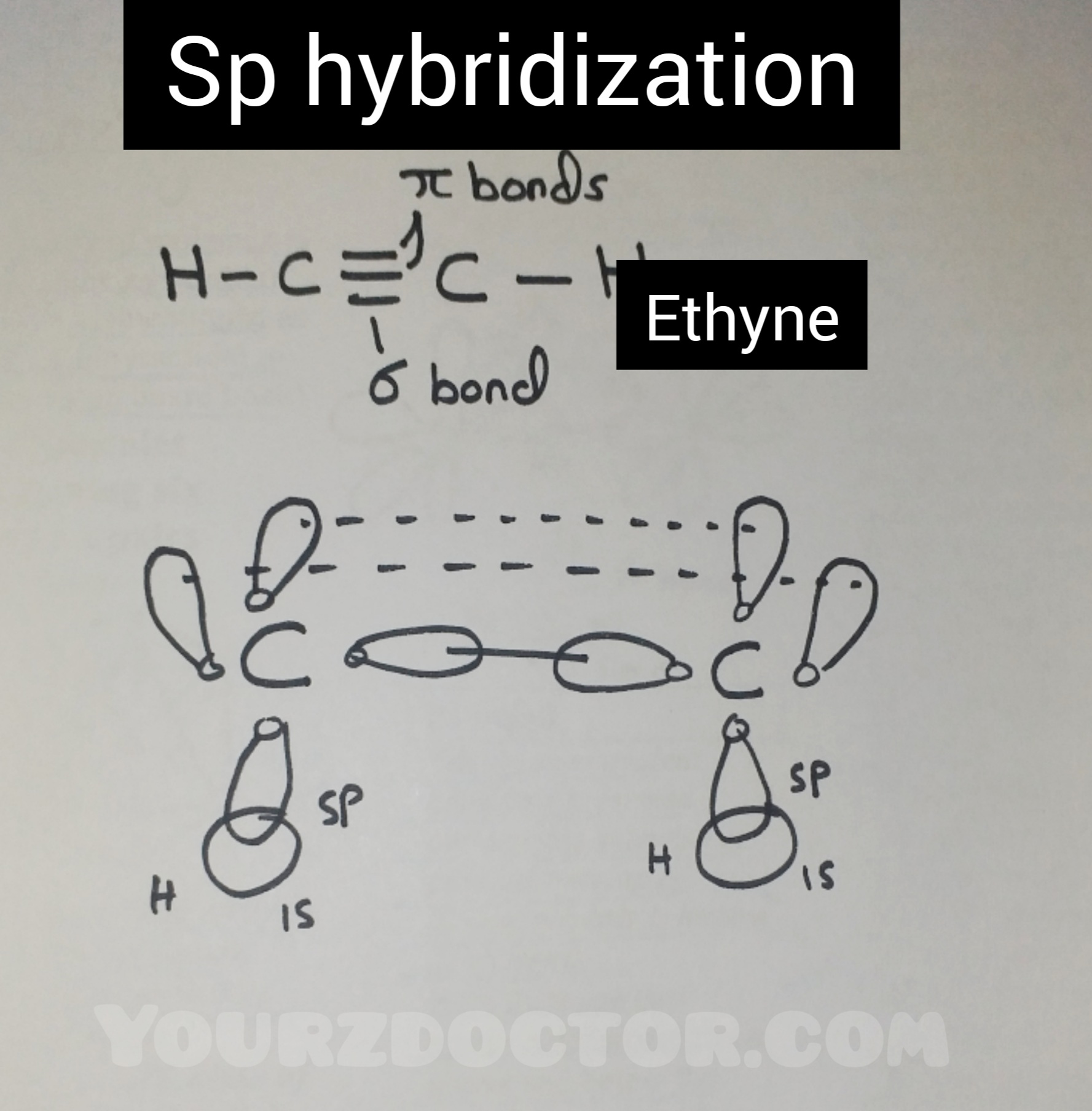
Sp hybridization:
The process
in which one S and one P orbital mix to form a new set of two equivalent sp hybrid
orbitals is known as sp hybridization.
E.g.
Ethyne
and beryllium dichloride are formed through sp hybridization.
Conjugation:
Conjugation
is the
• delocalization
of electrons
• impart
stability ( stability of ionic system)
• only
with pi bonds and lone pair
• No
relation with sigma bond.
That’s
means movement of electrons ( pi electrons or lone pair ) in saturated ( single
bond ) as well as in unsaturated double and triple bond ) system.
E.g. of saturated system
CH2-OCH3
CH2=OCH3
In the
saturated system the 0 have lone pair and
it will give the lone pair to C and make the double bond by conjugation.
E.g. of unsaturated system
CH2=CH-CH2+
+CH2-CH=CH2
In the
unsaturated system the movement of electrons from 1 carbon to 2 and then it is up
to 2 carbon to make bond with 1 carbon or 3 carbon then it will make double bond
with 3 carbon by conjugation.
Conditions for conjugation:
•all the atoms should be sp2 hybridized
•all
the p orbitals should be in same plane ( parallel to each other )
•p orbitals
are not orthogonal ( perpendicular) to each other
•conjugation
leads to decrease in energy of system therefore cause the stability.
Types of conjugation:
1)Linear
conjugation
2)Cross
conjugation
Linear conjugation:
In linear
conjugation all pi bonds participate in conjugation there is the transfer of electrons
is linear, transfer of electrons in one line.
E.g.
CH2=CH-CH=CH-CH=O
Cross conjugation:
When
out of 2 pi bonds participate in conjugation then this is called cross conjugation.
Linear
conjugation show more stability And linear conjugation is always greater than cross
conjugation.
Learn more
Related search
What is concept of hybridization?
What is hybridization?
Types of hybridization
Sp3 hybridization
Sp2 hybridization
Sp hybridization
Why hybridization occurs?
What is conjugation?
Conditions for conjugation
Types of conjugation
Linear conjugation
Cross conjugation







0 Comments